Teen Mental Wellness

What is Mental Wellness?
The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services recognizes that mental health includes a person’s psychological, emotional, and social well-being and affects how a person feels, thinks, and acts. Mental health disorders refer to a variety of conditions that affect mood, thinking and behavior.
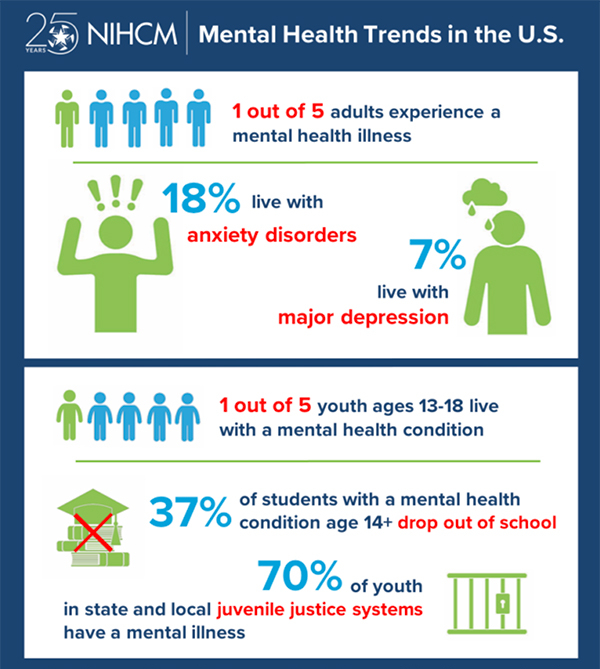
According to the World Health Organization, nearly one in every eight people in the world were living with a mental disorder in 2019. Anxiety and depressive orders are the most common. It is estimated that of the 2 million youth in the juvenile justice system, about 50-75% of them meet the criteria for mental health disorder. When compared to the 9-22% of the general youth population that have a diagnosable disorder, we can see that there is a prevalent mental health issue in the justice system.
Is There a Correlation Between Mental Health & Juvenile Crime?
Research has shown that youth with disruptive behavior disorders are more likely to be physically aggressive, and those with conduct disorders or attention/deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) are more likely to repeatedly offend during adolescence.
The most common mental health disorders in youth in the juvenile justice system are substance use disorder and high anxiety. Further, about 39% of the youth involved with the justice system are diagnosed with multiple disorders.
Those with a mental illness are three times more likely than the general population to interact with police and be arrested. Though causation has not been proven, many studies show that there is a high correlation between those with mental illnesses and involvement in the justice system. Thus, it is important to recognize the risk factors and know when to intervene.
What are the Risk Factors?
While the likelihood of developing a mental health disorder partially depends on genetics, there are also external risk factors that can contribute to someone developing a mental health disorder. For example, being exposed to poverty, violence, disability, and inequality can increase the risk for mental health disorders.
Due to the high rate of juvenile individuals with mental health issues in the justice system, it is important to get the help and support you need sooner rather than later. Combating mental health issues can help to prevent the likelihood of entering the juvenile justice system. Those with mental health can make more rational decisions and control strong emotions.
How to Support Your Teen
If you notice signs of mental health struggles in your teen, you can intervene and prevent the situation from getting worse. First and foremost, become familiar with the warning signs. These signs can include withdrawing from things they normally enjoy, a drastic change in weight, mood swings, or signs of drug, alcohol or substance use.
When you notice these signs, educate yourself on mental illness and speak to your child about what they are going through. Create an environment that feels safe for them and free from judgment. Encourage your child to share their feelings openly and be sure to be supportive rather than enabling. You can ask your teen what you can do to best support them through what they’re feeling.
Six Coping Skills to Try Right Now
The right coping mechanisms can help teenagers express their emotions in a healthy way, process strong feelings, and handle conflict.
Here are some simple coping techniques teens can try:
- Deep breathing
- Visualization
- Physical activity
- Creative pursuits
- Spending time with friends
- Spending time outdoors
Finally, consider setting up an appointment with your pediatrician or primary care doctor to see if they can provide a diagnosis or refer you to a mental health specialist. Early intervention and prevention are crucial to strengthen an individual’s ability to regulate their emotions. Prompt treatment can reduce the severity of symptoms or in some cases prevent major illnesses altogether.